ABAs, ACHs, EFTs… All these acronyms can be very confusing for mobile bank users. If you’re trying to transfer money, especially to loved ones living overseas, it’s crucial to understand what these terms mean.
The process of transferring money doesn’t have to be complicated or risky. In this article, let’s take a look at what an ABA number is, how it’s used, and how to find it.
What Is an ABA Number?
In 1910, the American Bankers Association (ABA) created the ABA routing number, a set of numbers used to identify a specific financial institution during the payment process.
Initially, it was only designed as a way to determine the check-processing endpoint. Today, it also identifies participants in automated clearing houses (ACHs), electronic funds transfers (EFTs), and online banking.
How the ABA number has changed.
Over the years, the ABA bank routing number has changed for several reasons, including the Federal Reserve System. Magnetic ink character recognition (or MICR code) was invented as a unique technology that could be used for processing checks. It consists of a nine-digit code that appears on the left side of the bottom of checks. The code identifies the bank and branch involved in the transfer of funds.
Laws that affect the ABA number.
In addition, the ABA routing number changed due to the implementation of the Expedited Funds Availability Act (EFAA) and the Check Clearing for the 21st Century Act (Check 21).
The EFAA is a law enacted in 1987 to limit how long banks can hold a check and other deposits before clearing them for payment.
While banks tend to hold checks and electronic deposits to ensure they aren’t returned unpaid, they must abide by the following maximum time holds:
- Up to two business days for checks from accounts at the same bank.
- Up to seven business days for local checks.
- More extended periods for purposes that are deemed reasonable.
Check 21 is a law that was enacted in 2004 to help banks electronically process more checks. It allows financial institutions to create electronic images of checks for faster processing. This process, called check truncation, also reduces the cost of processing paper checks.
In any case, it typically takes two to five business days for a check to clear unless the amount being cashed is large (greater than $5,000). Electronic payments and electronic transactions often occur within a shorter period than checks.
Learn more about sending money with Remitly.
What the Numbers in an ABA Number Mean
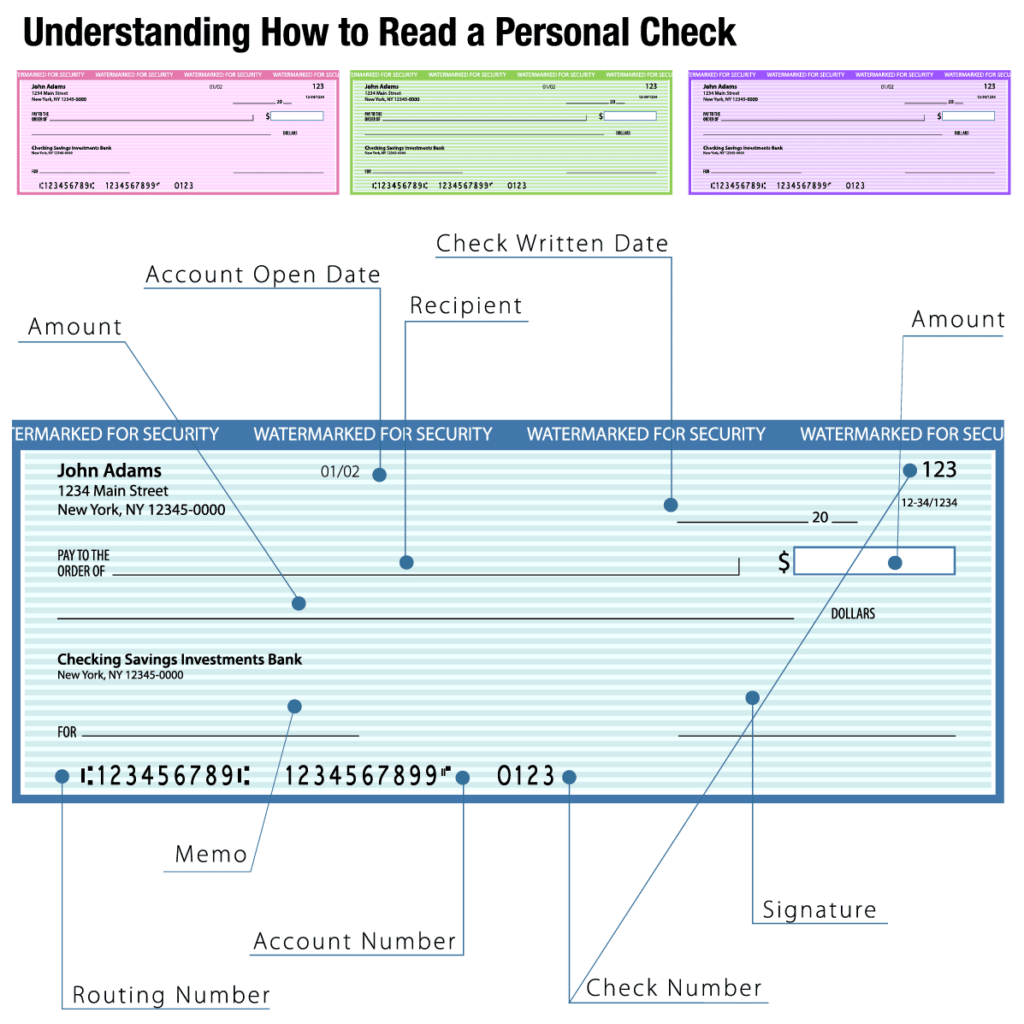
The ABA number, also known as the routing transit numbers (RTN) or check routing number, is part of the entire MICR code on a paper check.
The MICR string of characters comprises three parts from left to right on the check: a routing number, a bank account number, and a check number.
What an ABA routing number is.
The ABA number is the bank routing number, which is the first series of numbers on the far-left side of the MICR code. The routing number is printed with magnetic ink or MICR font that a computer uses to identify the bank or financial institutions associated with an account.
An ABA number doesn’t correspond to a particular type of account, so it can apply to checking accounts, savings accounts, and others.
The ABA routing number is made up of several parts:
- The first four digits identify the bank’s physical location.
- The fifth and sixth digits stand for the Federal Reserve Bank through which the electronic and wire transfers are routed.
- The seventh digit stands for the Federal Reserve check processing center the institution was assigned to
- The eighth digit stands for the Federal Reserve district.
- The last digit stands for a checksum, a value used to detect errors during data transfers.
How an ABA Number Is Used
The nine-digit ABA routing number is only issued to federal or state-chartered financial institutions in the United States. They must be eligible for an account at the Federal Reserve Bank to be given an ABA number.
The ABA number is the bank’s identification number. This identifier can be used to process checks, electronic checks, automated clearing house (ACH) transactions, electronic fund transfers (EFTs), and international wire transfers. This is also the same number often asked for when setting up direct deposits and automatic bill payments.
How to Find an ABA Number
Now that you know what an ABA number is, you’re probably wondering how to find it even if you don’t have any paper checks.
There are several easy ways to find an ABA number and its associated financial institution. You need to have a paper check, know the bank’s name, OR have access to your bank account online.
Find it via a check.
If you have a personal paper check, you can simply look for the nine-digit number along the far-left side of the bottom of the check.
A bank’s ABA is also found on the bottom of deposit slips in your checkbook. The number might be in a slightly different location if you’re looking for it on an e-check or a business check.
Look it up through a bank.
If you don’t have a paper check handy or you need the routing number for a debit card or credit card account, you can log into your account online to find it. The ABA number is usually found under direct deposit or ACH information.
If you don’t have an online account, you can also call the bank or look it up on its website. Be sure to use the correct number, as some banks have different ones for ACH, wire transfers, and direct deposit. If in doubt, confirm with the bank’s customer service representative.
Use an ABA number lookup tool
The American Bankers Association also offers a convenient ABA Routing Number Online Lookup Tool. You can enter the bank’s name and state to find the ABA number, or you can enter the ABA number to find out the bank.
Why an ABA Number Is Important
ABA routing numbers are essential for several reasons.
One, the ABA number allows financial institutions to trace where a money transfer is coming from and going to, making electronic processing more efficient.
Second, it eliminates potential errors that can cause transfer delays.
Last, you must safeguard your ABA number and bank account number to prevent thieves from making fraudulent transactions. When you send money internationally, we help you keep your Remitly account safe and secure.
